RFID in Warehouse Management 2
Introduction:
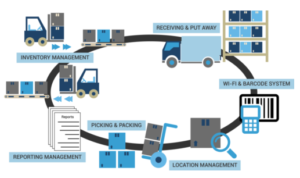
In modern logistics management, the warehousing process plays a crucial role. Traditional manual management methods are prone to errors, inefficiency, and require substantial manpower. However, the emergence of RFID technology has brought revolutionary changes to warehouse management. By combining RFID tags with items, warehouse managers can achieve accurate tracking, locating, and management of goods, thereby improving work efficiency, reducing errors, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Working Principle of RFID Technology:
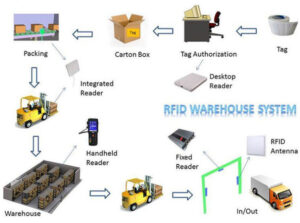
RFID technology consists of three main components: RFID tags, RFID readers, and a central database. RFID tags are miniature chips attached to items, capable of storing and transmitting information related to the items. RFID readers communicate with tags through radio signals and transfer the read information to a central database for processing and analysis. The central database stores all item information and their respective locations, providing real-time data support to warehouse managers.
RFID in Warehouse Management 3
Application Scenarios of RFID Technology in Warehouse Management:
Item Tracking and Locating: By utilizing RFID technology, warehouse managers can accurately track and locate the position of each item. Whether during the inbound, outbound, or transfer process, RFID tags can record real-time information on the status and location of items, thereby enhancing visibility and transparency in logistics.
Inventory Management: Traditional inventory counting requires a significant amount of manpower and time, and is prone to errors. RFID technology enables automatic inventory counting of all items within the warehouse, reducing human-induced errors and time costs, thereby improving the accuracy and efficiency of inventory management.
Automated Inbound and Outbound Processes: By leveraging RFID technology, warehouse managers can achieve automatic identification and handling of goods. When goods enter or leave the warehouse, RFID readers can automatically read the tag information and interact with the database, enabling automated inbound and outbound management, reducing human intervention errors and time delays.
Advantages and Challenges of RFID Technology:
RFID technology offers the following advantages in warehouse management:
Efficiency: RFID technology enables fast scanning and identification of a large number of items, enhancing the efficiency of logistics processing.
Accuracy: Compared to traditional barcode scanning, RFID technology can accurately read tag information without physical contact, reducing error rates.
Real-time Tracking: RFID technology allows real-time tracking and monitoring of item locations and statuses, providing timely data support.
However, RFID technology also presents some challenges in warehouse management:
Initial Costs: Deploying an RFID system requires an investment, including the purchase and installation of tags, readers, databases, and other equipment.
Tag Management: Managing and deploying a large number of tags may introduce complexities, such as tagging, replacement, and maintenance.
Data Privacy and Security: Data in the RFID system may involve sensitive information, requiring appropriate security measures to protect data privacy and integrity.
Conclusion:
RFID technology holds tremendous potential in warehouse management, enabling precise item tracking, locating, and management for warehouse managers. With advancements in technology and cost reductions, RFID technology will play an increasingly important role in warehouse management, providing more efficient, accurate, and reliable solutions for the logistics industry. However, it is important to recognize the challenges associated with RFID technology and actively explore solutions to promote its broader application and development.





